25
2023
-
07
Bud wheat feeding, how to better play its nutritional value
Recently, the continuous rainy weather in Henan, Shandong and other places has caused germination and moldy of wheat during the harvest period. Germinated wheat is basically not used as rations, and its price has also dropped significantly. When the price of wheat has obvious advantages over corn, the bud wheat is used in animal husbandry instead of corn after certain treatment. It can not only reduce the cost of feed, but also solve the problem of food stocks, and the economic and social benefits are huge.

However, once the wheat "sprouts", the energy reserves will begin to dry up, and the relevant indicators will change. At the same time, bud wheat is easy to form viscous chyme in the intestinal tract, which affects nutrient absorption and limits the proportion of bud wheat in feed.
1. Application of Bud Wheat in Broiler
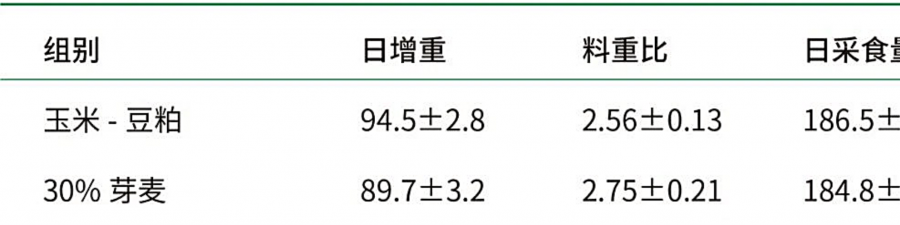
Using 30% sprout wheat instead of corn in the corn-soybean meal diet, the daily gain of large broilers decreased, the feed ratio increased, and the viscosity of small intestine chyme increased significantly.
Fig. 2 Effect of bud wheat on chyme of Zhongda broiler (Li Hua, 2011)
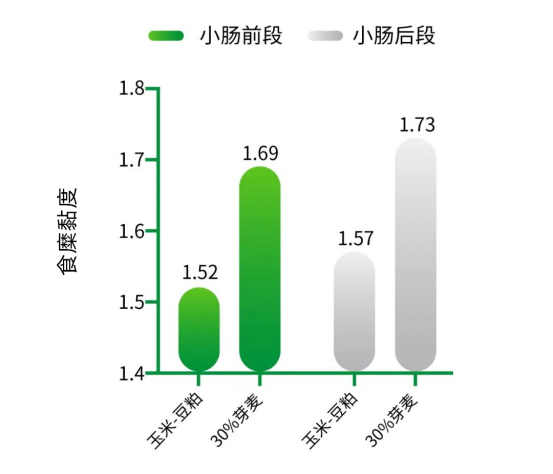
Table 2 Effects of bud wheat on production performance of Zhongda chicken (Li Hua, 2011)
2. Application of bud wheat in weaned piglets
Different proportions of germinated wheat were used to replace corn and soybean meal in the corn-soybean meal diet of weaned piglets. It was found that adding certain germinated wheat can improve the digestibility of crude protein, energy and calcium (Figure 3). However, the higher the amount of bud wheat, the better. When the proportion of bud wheat was more than 30%, the digestibility of protein and energy showed a downward trend.
Figure 3: Effects of different proportions of germinated wheat on nutrient digestibility of diets (Bai Yunfeng et al., 2016)
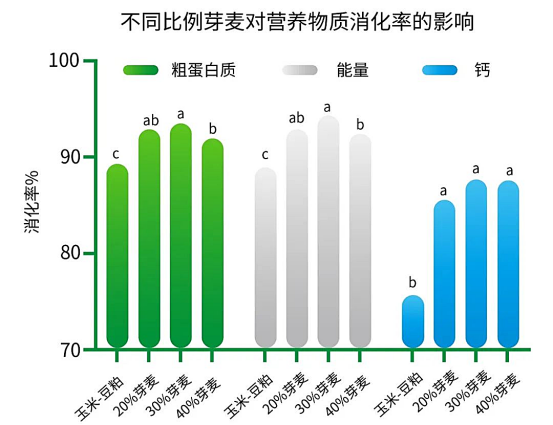
From the above, it can be seen that when the addition ratio of bud wheat is more, it is easy to cause the viscosity of chyme to increase, limit or affect the digestion and absorption rate of nutrients. Sticky manure, water and even diarrhea and other symptoms, resulting in a decline in livestock and poultry production performance.
In response to this situation, Blue Valley's micro-star product, Blue Lingweizhu, and full-price fermenters, solve a variety of problems brought about by the replacement of corn by bud wheat from the root and different dimensions.
Lan Lingwei Zhu
Lanlingweizhu can significantly improve the problems of fecal stickiness and anal paste caused by the addition of a large proportion of bud wheat in the feed.It is a highly efficient, stable, resistant and rapidly germinating combination probiotic produced by Blue Valley Microbiological Technology Co., Ltd. through its unique PCW WBB technology. According to the changes in the intestinal environment and the different points at which probiotics play the best biological effect in the intestinal tract, a large number of probiotics play a role in each intestinal tract.
probiotic bacillusGermination in the middle of the duodenum, acting on the small intestine, occupying space, producing enzymes, and promoting digestion and absorption of feed;temperature resistant lactic acid bacteriaProliferation in the jejunum segment, acting on the posterior jejunum, producing acid, inhibiting bacteria and resisting stress;Clostridium butyricumIt mainly germinates in the lower ileum, mainly acts on the large intestine, producing acid and repairing intestinal cells to inhibit Clostridium.
Product Information
【Product Ingredients 】: Clostridium butyricum, lactic acid bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, total effective live bacteria ≥ 7.5 billion cfu/g.
[Usage and dosage]: 200g ~ 500g is added to each ton of full feed, and fed after being fully mixed and evenly.
[suitable feeding object]: weaned piglets, broilers, laying hens and other breeding animals.
Product efficacy
1, to achieve the whole intestinal protection, enhance the intestinal barrier function
2, reduce the daily grain emulsion viscosity, improve nutrient absorption
3, reduce fecal viscosity, reduce environmental pollution
Product layer empirical sharing.
According to the breeding experiment of Lanlingweizhu laying hens, the use of 50% wheat instead of corn in the feed caused diarrhea in 283-day-old laying hens, and the laying rate also dropped sharply. The diarrhea rate was significantly reduced and the egg production rate was restored in the wheat group after adding 300 g/t Blue Lingweizhu for a week.
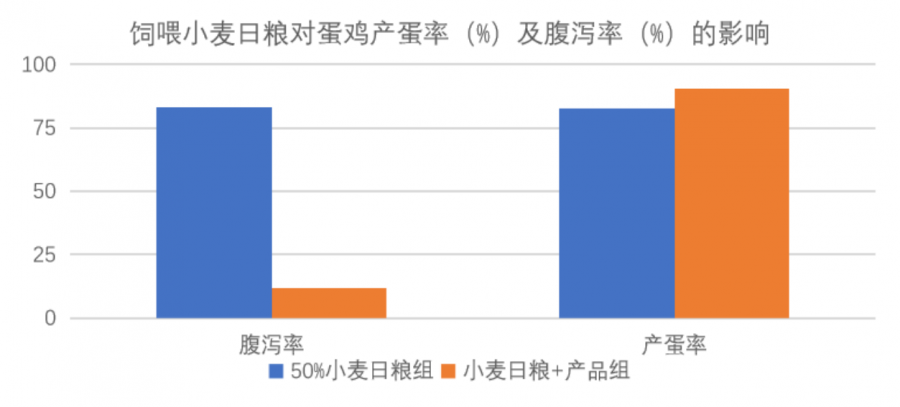
After the wheat experimental group returned to normal, the product was stopped, and 3 days later, diarrhea began to increase.
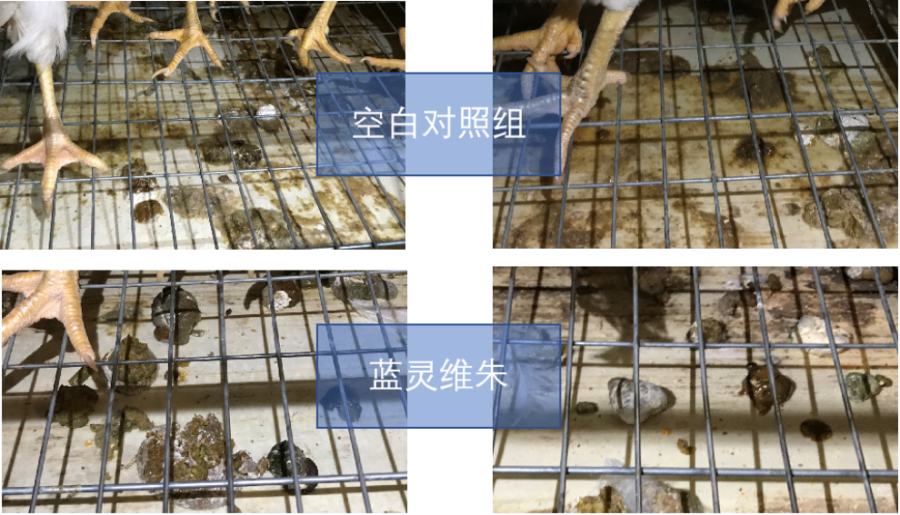
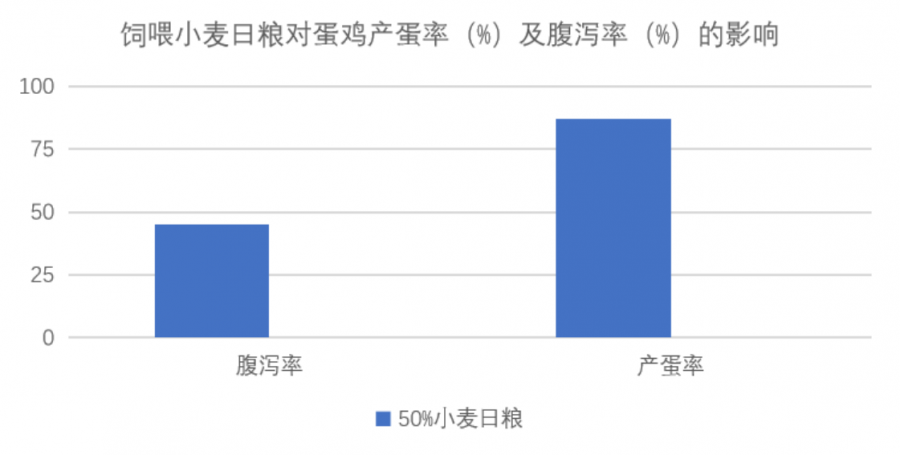

Therefore, although the bud wheat energy value decreased more, and the viscosity is larger, but through the use of blue Lingwei Zhu, can solve the chyme hair sticky, improve intestinal diarrhea, promote nutrient absorption, further play the bud wheat huge price advantage, help optimize feed costs.
At the same time, the full-price material fermentation agent in the blue valley can be directly fermented and fed to the bud wheat, which can improve the utilization rate of digestion and absorption after fermentation and effectively reduce the cost.
full-price fermenter
Fermentation Scheme
Taking 60% wheat + 20% soybean meal + 20% bran as substrate and controlling the ratio of feed to water at 1:0.35, the main indexes changed as follows:
(Due to the different control of raw materials and fermentation conditions, there are some differences in the indicators after fermentation).
1) The pH value drops to about 4.5;
2) Reducing sugar ≥ 3%;
3) Small peptide content ≥ 18%;
4) produce a large number of organic acids, active bacteria, digestive enzymes.
5) The highest biomass of Lactobacillus ≥ 8 × 10.8 billion/g

Benefits and Significance of Fermentation
1) low moisture fermentation, to ensure good fermentation effect at the same time, increase the amount of addition in the feed, effectively reduce the cost.
2) the color sensory state is good, after fermentation, the flavor is good and the food is strong.
3) The enrichment of high-density Lactobacillus and its metabolites is more conducive to animal intestinal health.
4) The energy loss in the fermentation process is small, and the macromolecule NDF and other polysaccharides are degraded and retained in the fermentation material in the form of lactic acid and reducing sugar, which is more conducive to the absorption and utilization of animals.
5) Solve the viscosity problem of the fermentation material production process and the finished product, and facilitate the production and use of the fermentation material.
application method and effect
Application method: add 2%-5% fermentation mixture to the whole feed.
Use effect:
1) good flavor, strong inducement, improve feed intake;
2) Improve the egg production rate, extend the peak of egg production, and improve the efficiency of breeding;
3) Improve egg quality, reduce fishy smell, and have good egg yolk color;
3) Improve and maintain intestinal health and reduce the occurrence of intestinal diseases;
4) Reduce the ammonia odor in the enclosure and improve the breeding environment.
Matters needing attention when using bud wheat
1, control of moisture, moisture below 12.5% germination process will stop, high moisture is not conducive to storage.
2. The integrity of starch is destroyed during wheat germination, which may affect feed pelleting. Pay attention to adjusting production parameters.
3, a reasonable assessment of its nutritional value, pay attention to the control of mycotoxins.
4, according to the use of other raw materials, select the full-price material fermentation agent to improve feed utilization efficiency and improve animal health.
5. When feeding ruminants, the starch degradation rate of bud wheat will increase to a certain extent. Pay attention to the amount of use to reduce the risk of acidosis.
Related News



